3 Different Textures of BHO And How They’re Made

Wax, sugar, shatter, and honey oil all start the same way. What makes them look and behave differently comes later. If you’ve ever noticed how differently BHO can appear from one product to the next, you’re seeing the result of refinement rather than extraction. The oil itself is created through the same closed-loop process, but it doesn’t leave the system finished. Those post-processing choices are what give BHO its range of forms, even though the starting point remains the same. Those variations all trace back to the same starting point. To understand how BHO takes different forms, it helps to first understand what BHO is.
BHO Meaning: Butane Hash Oil
Butane hash oil (BHO) is a powerful cannabis concentrate created by using butane to extract cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant. Butane is a colorless, highly flammable hydrocarbon gas that easily shifts from liquid to gas at low temperatures, making it useful as a solvent but hazardous without controlled handling.
BHO extraction is the process of using liquid butane to dissolve resin glands from cannabis flower, creating a cannabinoid- and terpene-rich oil.
BHO concentrates come in several popular forms, each offering a distinct texture and experience. Known for its high THC content and terpene-rich profile, BHO is typically consumed by dabbing or vaporizing.
BHO Textures Explained: Wax, Sugar, and More
BHO textures are determined during post-processing, not during the initial extraction itself. After butane hash oil is extracted in a closed-loop system, the oil is still rich with solvent. At this stage, technicians can influence the final texture by carefully adjusting temperature, agitation, and purging techniques.
BHO Wax

BHO wax has a soft, opaque appearance and a whipped or butter-like consistency. This texture is typically created by introducing agitation or controlled heat during purging, which causes the oil to nucleate and trap air. Wax is often chosen for its ease of handling and uniform structure.
BHO Sugar

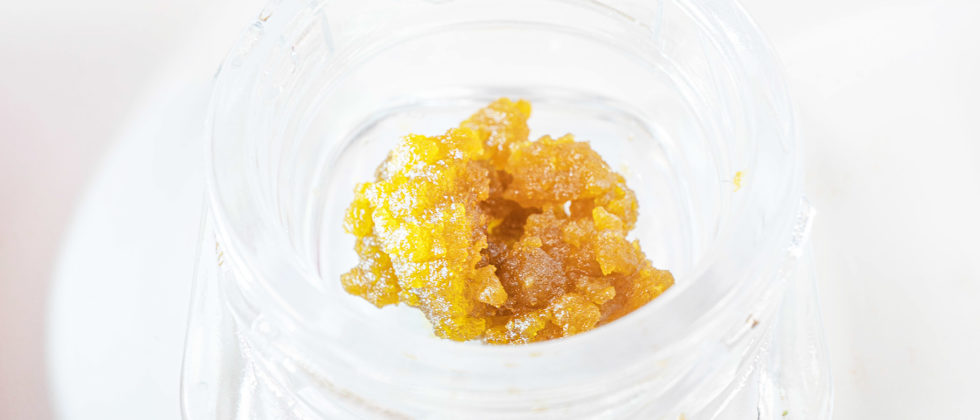
BHO sugar has a grainy, crystalline appearance suspended in terpene-rich sauce. This texture forms when cannabinoids begin to crystallize during post-processing while terpenes remain in liquid form. The result is a visually distinct concentrate with a granular structure.
Shatter

Shatter is known for its translucent, glass-like appearance and brittle consistency. It typically forms when the oil is purged slowly and left undisturbed, allowing cannabinoids to solidify into a stable sheet. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can influence how stable shatter remains over time.
Crumble

BHO Crumble is drier and more porous than wax, breaking apart easily into small pieces. This texture is often the result of extended purging or additional agitation, which removes more residual solvent and creates a less dense structure.
BHO Honey Oil (Sap)

BHO honey oil, sometimes called sap, has a thick, sticky, and viscous consistency. This texture occurs when the oil retains a higher terpene content and remains in a semi-liquid state after purging. Honey oil flows slowly rather than holding a firm shape.
Each of these textures offers a different balance of appearance, stability, and handling preference, but they all come from the same butane hash oil extraction process.
Why Use Butane for Cannabis Extraction?
Butane is favored over other solvents, such as CO₂ or propane, because of its physical properties:
- Low boiling point: Butane evaporates at around 33 degrees Fahrenheit, allowing extractors to purge solvents at very low temperatures.
- Flavor preservation: Low-temperature purging helps protect delicate cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids.
- Non-polar solvent: Butane does not pull water-soluble compounds like chlorophyll, resulting in a cleaner concentrate.
- Efficiency: Butane dissolves trichomes quickly, producing high yields with strong terpene retention.
What Does Closed-Loop Extraction Mean?
A closed-loop extraction system is a sealed network of vessels that uses pressure and thermodynamics to move solvents safely through cannabis material without releasing gas into the environment.
A professional system typically includes:
- Solvent tank: Holds chilled liquid butane
- Material column: Contains cannabis flower
- De-waxing column: Removes fats and lipids
- Collection base: Captures the extracted oil
The system continuously recycles butane, completing the “loop” and dramatically reducing risk. This is now considered the gold standard for solvent-based cannabis extraction.
How Butane Hash Oil Is Made (Professional Process Only)
Behind every smooth dab is a highly controlled, multi-step process that should only be performed in licensed facilities.
Step-by-Step: How BHO Is Made
Step 1: Preparing the Flower
The process begins with cured, hand-broken cannabis flower loaded into a stainless steel material column.
Step 2: Pressurizing With Butane
Chilled nitrogen pressurizes the system, pushing liquid butane into the material chamber. Once internal pressure reaches the right level, the butane flows through the cannabis, fully saturating the material.
Step 3: Dissolving Resin
As the butane moves through the flower, it dissolves resin glands (trichomes) containing THCa, cannabinoids, and terpenes, creating a cannabinoid-rich solution ready for refinement.
Step 4: Dewaxing the Extract
To remove unwanted plant waxes and lipids, technicians transfer the solution to a dewaxing vessel chilled to –80 °C. Here, fats coagulate and separate, leaving behind a cleaner oil.
Step 5: Butane Recovery
The solution moves to a collection base warmed by a water jacket, evaporating and re-condensing the butane for reuse. What remains is pure, potent cannabis oil.
Step 6: Final Collection
The concentrate is collected, then purged, tested, and packaged as shatter, wax, or budder.
Every stage is carefully monitored for temperature, pressure, and purity to ensure safety and consistency.
Is BHO Safe to Consume?
When professionally made, BHO undergoes lab testing to ensure residual solvents remain below safe thresholds. Always look for concentrates with verified lab reports showing potency, residual solvents, and contaminant levels.
Unregulated or homemade extracts, however, may contain dangerous impurities. Licensed producers must meet strict testing requirements before concentrates can be sold to consumers.
When purchased from licensed dispensaries, BHO products are both potent and safe for consumption.
BHO vs Live Resin: What’s the Difference?
One common point of confusion is the difference between BHO and live resin.
- BHO is typically made from cured cannabis flower.
- Live resin uses flash-frozen cannabis harvested at peak freshness to preserve more volatile terpenes.
Both products may use butane extraction, but the starting material creates noticeable differences in aroma and flavor.
BHO vs. CO2 Extraction: What’s the Difference?
| Extraction Feature | BHO Extraction (Butane) | CO2 Extraction |
| Flavor Preservation | Excellent | Moderate |
| Solvent Use | Yes (butane) | Yes (CO2) |
| Purge Temperature | Low | High |
| Yield | High | Moderate |
| Safety Requirements | Higher | Moderate |
Both methods produce clean concentrates, but BHO’s ability to retain delicate terpenes makes it the top choice for flavorful, high-potency dabs. CO2 extraction, by contrast, is more common in vape cartridges due to its versatility and clean reputation.
Frequently Asked Questions About BHO
What is BHO hash oil made from?
BHO is made from cannabis flower or trim using butane to extract cannabinoids and terpenes.
What is BHO wax or BHO sugar?
These are textures created during post-processing, not separate extraction methods.
Is making BHO at home legal?
No. Unlicensed extraction is illegal and dangerous.
Is BHO stronger than other cannabis products?
Yes. BHO commonly ranges from 60 to 90 percent THC.
Experience BHO Differences for Yourself
Understanding BHO textures comes down to recognizing how refinement shapes the final product. Wax, sugar, shatter, and honey oil all begin as the same butane hash oil, but the choices made after extraction determine how each one looks, handles, and stabilizes over time. Those differences are intentional, controlled, and part of what gives BHO its versatility.
Seeing these textures side by side is often the best way to appreciate how post-processing influences the final result. From softer, whipped forms to more structured or viscous finishes, each expression reflects a different approach to refinement rather than a different extraction method.
Ready to explore BHO in its many forms? Browse the Terrapin Dispensary Menu to see available concentrates, or learn more about professionally crafted extracts by visiting the Double Bear website.